Table of Contents
Introduction on Liquids: States of Matter
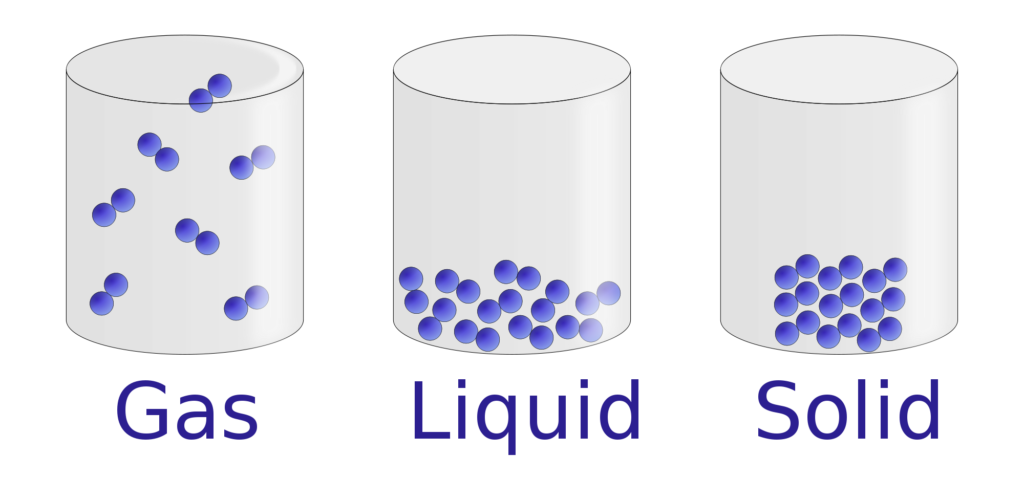
Liquids are among the states of matter. Other states of matter are Solids, Gases, Plasmas, and Bose-Einstein Condensates. The complete information on Liquids is too vast that it would be more than a 1000 page book. But we’ll try to cover the most essential stuff in this article.
This Complete guide on liquids will help you to get the above basic understanding of liquids and the states of matter. Along with this, you will also be getting to know different properties of all states of matter specially Liquids – States of matter

Introduction – Cont.
Generally, in order to identify whether a substance is a liquid or other states of matter, the best way is to pour it from one container to another container. If it takes the shape of the new container, it would generally signify to be in the liquid state. So we can say in another way that, liquids take the shape of the new container when poured.
For example, if we pour a glass of water into another glass of different shapes and sizes, you will notice that the water is getting the shape of the new glass.

Small Exercise – Figuring out what substances are Liquids: States of Matter
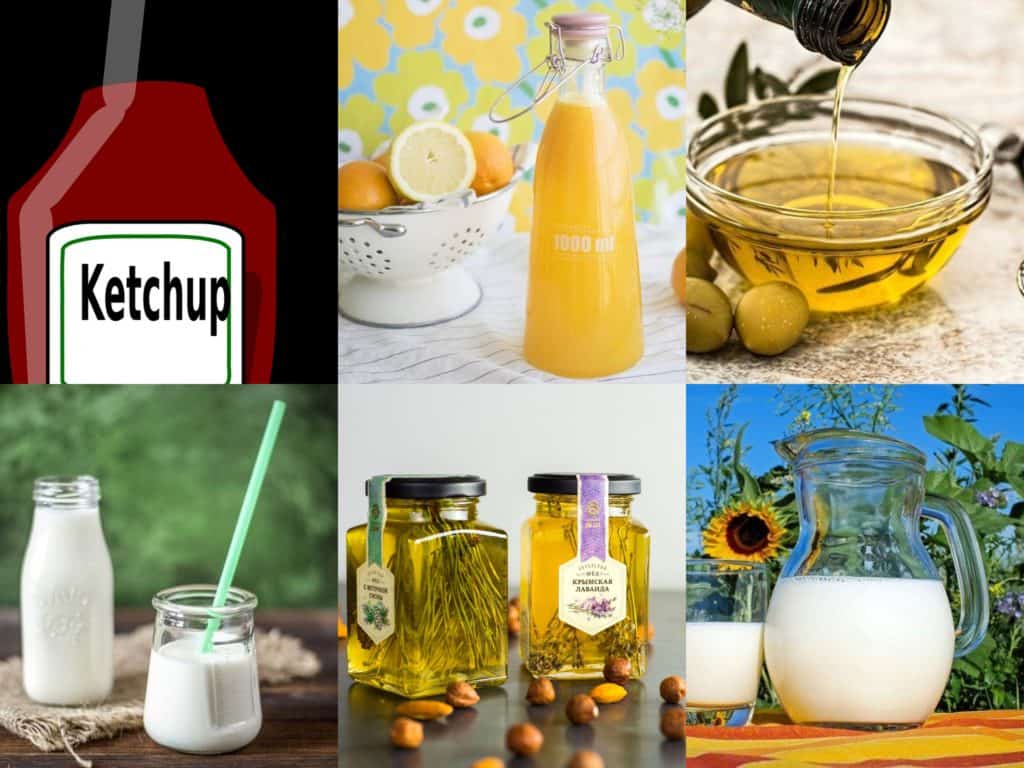
Considering this property of liquid in mind, kindly identify if the below list of items are Liquids – States of matter or not :
- Juice
- Milk
- Oil
- Tomato Sauce
- Honey
- Custard

Juice and Milk
So now, from the above items, Juice and Milk, we usually pour into the glass or container and it takes the shape of the same glass or the container. So we can now say that Juice and Milk are both Liquid.
Oils
Oils too when poured in a glass / container / vessels, would take its shape. So Oils will also be categorized into the Liquid category. But if we compare the oil with the water or juice, it would be thicker. The reason behind that would be its viscosity. Oils would have more viscosity as compared to water or juice resulting in the thicker fluid.
Tomato Sauce, Honey, and Custard
Tomato Sauce, Honey, and Custard, on the other hand, are categorized as special liquids which are generally called Non – Newtonian Fluids. They actually behave like liquids and in many circumstances behaves the property of the solids.
For Example, if you turn your tomato sauce bottle upside down, sometimes, nothing comes out. So in this scenario, it behaves the property of the solids.
But now if we shake it and squeeze and then move the bottle upside down, by applying external hand forces and stress to it, you will visualize that tomato sauce will be coming out freely, following the property and characteristics of the liquid. Few people call these liquids as Semi – Liquids.
The same is true with honey as well. There are some sorts of uncooked custard that act like solids if you hit them, and the more force you put on, the tougher and harder the custard becomes.
What actually makes a Liquid a Liquid?
The Liquids – States of the matter is a midway phase between solids and gases. Just like the solids, particles in liquids are subjected to the intermolecular force of attraction as well.
But, the liquid molecules have more inter-molecular spaces between them, so they are not fixed on their positions, unlike solids.
The particle’s attraction in liquids keeps its volume to be constant, but the movement of these particles enables the liquid to conforms to the shape of the new container/vessels/glass (when poured).
The liquids will flow and fill the deepest portion of a container, taking on the shape of the container but making the volume to be constant.
The small amount of space between the particles means that liquids have very partial compressibility.
Essential Properties of Liquids: States of Matter
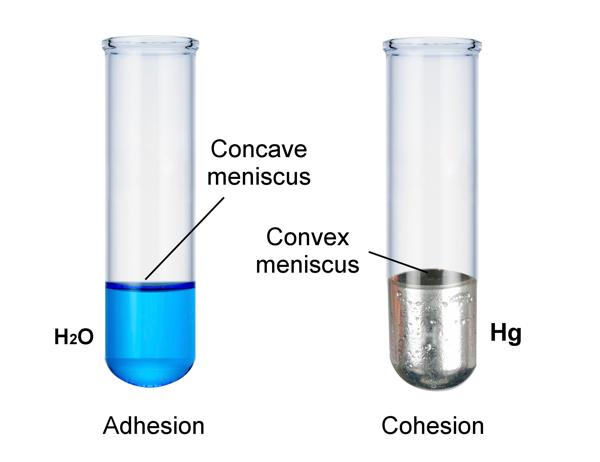
Cohesion & Adhesion
Before we get into cohesion and adhesion, it’s very important to know what does this two-term actually mean.
So Cohesion is basically a tendency for the same kind of particles to attract with each other. The Cohesive forces signify the surface tension of the liquids.
Surface tension is basically a very thin surface of particles that are highly attracted to one another than the particles surrounding them.
Till these forces of attraction of particles are not disturbed by external forces, they are strong and remain intact.
For example, the surface tension of water if high and is around 72 dynes/cm at 25°C. To know more about the surface tension of water and other liquids click here.
So Adhesion is basically a tendency for the different kinds of particles to attract each other. The particles of the liquids are generally not only attracted by the with one other but also get attracted to the other particles surrounding them like the walls of the container.
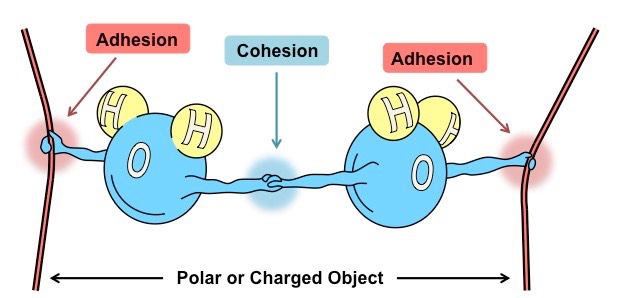
The combination of both cohesive & adhesive forces means that meniscus (concave curve) exists on the surface of the liquids. Adhesion implies for the capillary action when a liquid is drawn up into a narrow pipe or tube.

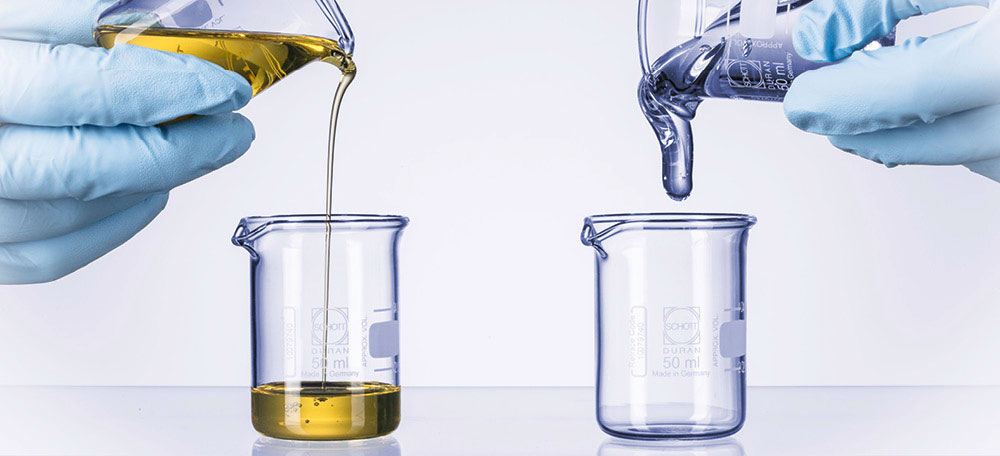
Viscosity
Viscosity is basically the terminology used to identify the resisting force to move the fluid freely. The fluid that flows quickly implies to have low viscosity, while the fluid that flows too slowly tends to have a high viscosity.
Now, the fluid that has more viscosity would be thicker and so, it tends to flow slow. Similarly, low viscosity fluids would be thinner and will tend to flow fast.
For Example, tomato sauce and honey have high viscosity resulting in having thicker particles and will tend to flow slowly as compared to water that has a low viscosity.
To know more about the viscosity of liquids, Click Here.

Evaporation
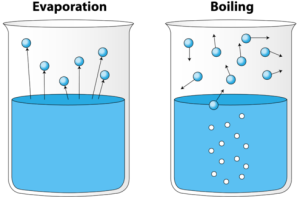
Since we now know that the particles of the liquid are always in constant motion, they generally collide with each other and along with the sides of the container as well.
But, when an ample amount of energy is transmitted to the particles at the surface of the liquid, it will overcome the surface tension holding it to the rest of the liquid.
Generally, the evaporation starts when the surface particles of the liquid gain enough kinetic energy to move away from the system.
As soon the particles escape the system, the remaining particles will have lesser kinetic energy and the temperature of the liquid lowers down. This process is called Evaporation cooling.
Volatility
Volatility signifies how simply a matter will vaporize i.e either turn into a gas or vapor form. A volatile substance is basically the one that evaporates easily at regular temperatures and having measurable vapor pressure.
Generally, we signify the term volatile to liquids. However, there are many solids that can turn directly into vapor without turning into liquids and are often referred to as “Sublimation”.
There is a terminology of the evaporation rate of a substance that indicates the rate at which a substance vaporizes under a fixed set of boundary conditions.
Now, If you Increase the temperature of the substance, it would become more volatile. More the concentration of flammable vapor, the greater will be the chance of the explosion.
Frequently Asked Questions
People also Ask
Liquids are basically made up of tiny vibrating particles under inter-molecular forces of attraction. Just like in the gaseous state of matter, liquids are able to flow and take the shape of the container.
Sand is basically a solid-state of matter. Its because each of its particles is in solid-state and their intermolecular forces of attraction are too strong as compared to liquids and gases.
Liquids have the same volume but can change their shape and size unlike solids
they have inter-molecular forces of attraction between solids and gases.
Liquids can take the shape of the container when poured into it.
Some of the examples of liquids are blood, water, milk, wine, oil, acetone, etc.
Honey is a supercooled liquid when stored lower than its melting point. At extremely minimal temperatures, honey does not freeze up solid, rather its viscosity boosts. Like most viscous (thick) liquids, the honey becomes thick and sluggish with decreasing temperature


Great content. Many new things came to know.
Good article, i had most of my doubts getting cleared with this article. Thanks a lot Science Clear for such great contents. Keep Going like this !! Looking forward seeing more articles from you !!
[…] Liquids: States of Matter – Complete Guide […]
[…] simple words, we can say that any hydraulic source especially water (a liquid state of matter) that generates electricity can be termed as […]