We know that light travels in a straight manner. Did you ever think that if light travels in a straight line then how are we able to see objects? Or if we switch on the light in the adjacent room the light can come inside our room too? Apart from travelling in a straight line, the light goes for another path also. This another path of light is caused due to a phenomenon called diffraction of light. Not only light but otherwise also go through diffraction. We know that that light can travel both have to wave and rate this phenomenon is applicable in light.

We are here to learn about what is diffraction how it is caused and other science-related stuff with it. Let’s start by knowing the meaning of it.
Table of Contents
What does Diffraction of light mean?
The word deflection was coined by an Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi in 1660. The bending of light around the corner of an obstacle and spreading of the light wave into the geometrical shadow of that obstacle is called diffraction of light. In simple words when the light comes across any obstacle or sharp edges it bends and changes part is known as the diffraction of light.

The satisfactory explanation of this theory is based on wave theory by Fresnel. According to him the wavelength of light is extremely small that we cannot see the bending of it around the corner this rectilinear propagation of light is only an approximation.
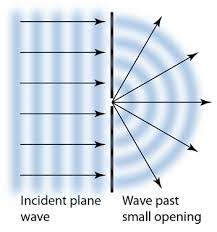
According to the wave theory of the Huygens-Fresnel principle, each point of a propagating wave is a set of spherical wavelets that can generate new waves. This is demonstrated in the above picture.
This phenomenon of diffraction is only visible in one criterion. This occurs when the size of the obstacle is compatible with the wavelength of the light.
Some factors like wavelength affect the rate of diffraction. The wavelength of light is directly proportional to the rate of diffraction. This means that if the wavelength of the propagating wave increases the rate of refraction increases too.
Different kinds of Diffraction of light phenomena
The type of diffraction which is observed in light is not only a single time. Two different kinds of diffraction can take place. The first one is Fresnel diffraction and the other one is Fraunhofer diffraction.
Although they are almost the same, there are some minor differences between them. Latest take a look at how they are different from each. You can see the difference between both diffraction phenomena in the table below.
| Fresnel diffraction | Fraunhofer diffraction |
| Either the source or the screen or both are at a finite distance from the obstacle. | The source of light and the screen are at infinite distances from the obstacle. |
| The incident wavefront is in the shape of a sphere or a cylinder. | Here, the incident wavefront is generally plane. |
| The center of the diffraction pattern formed due to this diffraction phenomena can be bright as well as dark depending on the number of fresnel’s zone. | The center of the diffraction pattern is always bright. |
| We can observe this diffraction in real life. | This is not a common phenomenon to be observed. |
Now we know the differences between Fresnel diffraction and Fraunhofer diffraction. Let us start by knowing both of them separately.
Fraunhofer diffraction
This type of diffraction arises when the source of light and screen is effectively at infinite distance from each other. This means that we cannot place an object at an infinite distance as we don’t know what is infinite. Meaning we haven’t calculated the value of infinite so if the object is far away from the diffracting aperture then Fraunhofer diffraction takes place.

You can see the diffraction pattern of Fraunhofer diffraction in the picture above. This diffraction pattern is further observed by setting up using a different number of slits.
Fraunhofer diffraction using a single slit
In this setup, a single slit is used to generate the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern. The slate used in this setup is of rectangular aperture whose length is larger than its breadth. The slit width should be comparable with the wavelength of the light and it should be never less than the light wavelength.

In the above picture, you can see how light passes through a single slit and form the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern. The study of the diffraction pattern is based on the superposition principle of Huygen’s secondary wavelet generation principle. This diffraction phenomenon was named after Joseph von Fraunhofer, but he is not completely responsible for the development of this theory.
When the Fraunhofer diffraction was performed using a single slit, a diffraction pattern with Central bright fringe and alternative dark and bright fringes are formed.
The equation for finding the intensity of fringes in the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern is:- I= (A2a2sin2X)/X2
In the above equation, I is the intensity of light, A is the amplitude, and X is the angle between the incident and refracted rays.
There are some conditions of forming of maxima and minima in any diffraction pattern. These conditions are interrelated with the parameters of the above equation. Let us see the condition of maxima and minima of Fraunhofer diffraction pattern.
Condition for maxima and minima
For finding maximum or minimum the equation of Fraunhofer’s diffraction is used. The first derivative of the equation is found and then it is equated with zero.
d(A2a2(sin2/X2)/dX=0
The conditions are:-
- X= infinity
- sinX=0
- X cosX – sinX=0
By the above parameters, the condition for maxima and the other successive minima are given by:-
Φ1 =∓ λ/a, Φ2 =∓ 2λ/a.. and so on.
Fraunhofer diffraction due to double slit
The diffraction pattern due to the double-slit consists of diffraction fringes caused by rays diffracted from two slits. Theses are superimposed on the interference fringes caused by rays coming from each pair of corresponding points on the two slits.
In this arrangement, two slits are placed parallel on the same plane. The width of each slit is generally identical and much smaller than their lengths. The space between the slits is opaque, and the distance between the slits is of the order of the wavelength which is used.
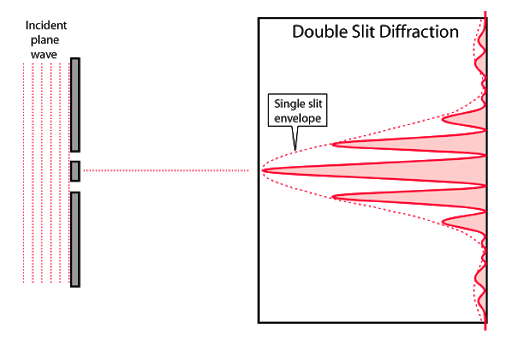
In the above picture you can see that, in double-slit diffraction, there are more high and low peaks than a single slit. You can also see that a whole bunch of high peaks are equal to a single peak in a single slit in terms of width.
The equation for finding the intensity of fringes in Fraunhofer diffraction pattern with a double-slit is:- I= 4Io(sin2X/X2)cos2Y, where Y is πdΦ/λ.
In this diffraction pattern, the series of maxima and minima are different. The successive minima are :- λ/2(a+b), 3λ/2(a+b), 5λ/2(a+b),…..
The successive Maxima are:- λ/(a+b), 2λ/(a+b), 3λ/(a+b),…..
Effect of different factors on the double-slit diffraction pattern
many factors like the street width, slit separation, the wavelength may affect the double-slit diffraction pattern. Here are some examples of how this factor alters the pattern.
- The space between the fringe pattern and the fringe is directly proportional to the wavelength. this means that if the wavelength will increase then the distance between the fringe pattern and the fringe will increase and vice versa.
- If the slit width is increased then the pics of the pattern become Sharper.
- If there is an increase in the slit separation by keeping the slit width constant then the fringe becomes closer together.
Difference between the single slit and double-slit diffraction of the light pattern
Even though both the diffraction pattern is part of the Fraunhofer diffraction pattern, but there are differences. By reading the above section you got to know that there are many differences in them. Latest list those differences together.
| Single slit | Double-slit |
| In this pattern the central is maxima. | In this pattern the central fringe pair of both maxima and minima. The intensity of the central diffraction Maxima is 4 times the intensity of the central Maxima due to the definition of all single slit. |
| On both sides there are maximum and minimum was whose intensity decreases gradually with distance. | The intensity of the central diffraction Maxima is 4 times the intensity of the central Maxima due to the definition of all single slit. |
| The spacing of diffraction maxima and minima depends on the slit width. | The spacing of maxima and minima depends on both slit width and slit separation. |
Fresnel diffraction
This is formed when the source and the screen are close to each other or the distance between them can be measured. This diffraction is based on the approximation of Fresnel diffraction that can be applied to the propagation of waves in the near field.
Equation of the Fresnel diffraction is four near field diffraction. the equation is used to calculate the deflection pattern made by waves passing through an aperture or around the object when viewed very close to the object.

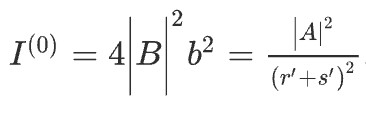
in this equation
History of Fresnel diffraction
The earliest work which can be said as the starting of this diffraction pattern was carried out by Francesco Maria Grimaldi during the 17th century in Italy. This work is mentioned in his monograph called “Light”.
After this, Richard C. MacLaurin explained the Fresnel pattern using the propagation of light and Huygen’s principle of superposition. The wavefront which goes forward from the slit to the detection screen originates from another wave somewhere from the gap on the same wavefront.
The gap is very small that only bright fringes can be produced by it. If somehow the gaps are made bigger than darker fringes will be produced until and unless no fringes can be detected.
MacLaurin does not say that the center of rings that are formed can be Black. But he mentioned that shadow can be produced by small circular objects in the rings.
The Fresnel diffraction integral
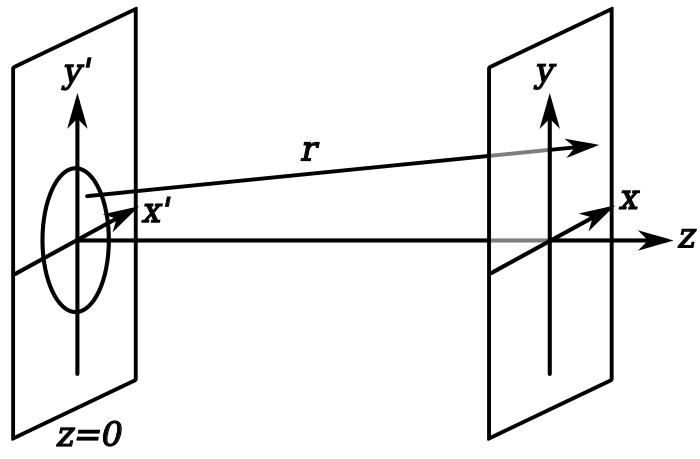
The above picture is the setup of the Fresnel diffraction pattern. based on the observation of mathematical theory was made which is called the Fresnel diffraction integral.
According to the picture above, the electric field at point (x,y,z) is given by:-

Where, E(x’,y’,0) is the electric field at the aperture., K is the wavenumber (2π/λ), I is an imaginary unit and
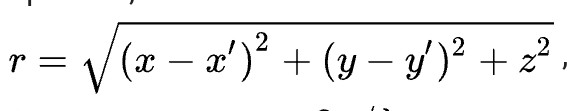
The Fresnel approximation
The main issue while calculating the Fresnel integral value was the outcome of r. by using the substitution formula the value of r was found to be a binomial expression. It was found, if the value of r is considered to be binomial then there is no approx value for r. By considering these parameters different value of z (a part of the equation for r) was found for different diffraction patterns. This can be seen in the graph below.
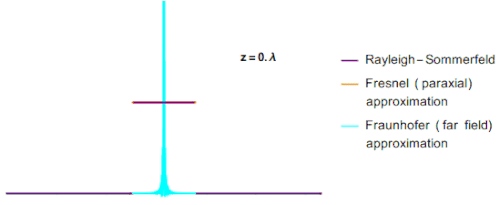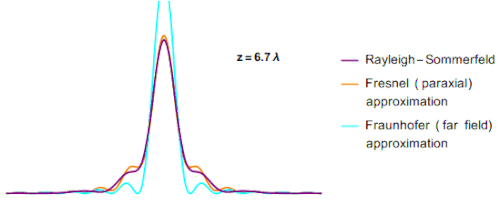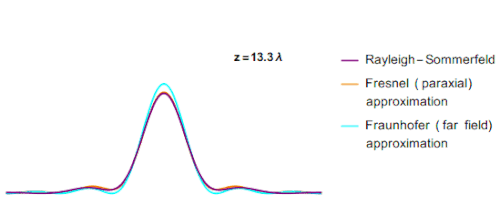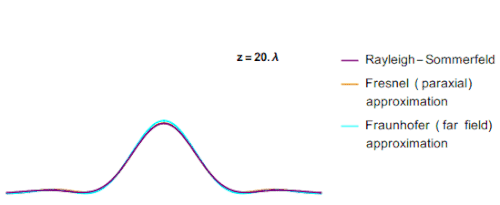
In the above GIF, you can see that with changing the value of z the value of r changes, and hence the peak of the graph also changes.
Diffraction due to plane diffraction grating (or N slits)
A diffraction grating is an arrangement that consists of a large number of parallel sides of the same width and separated by equal space. The space of the spacing is opaque. We can also say that it is a structure of alternate transparent and opaque spaces.
A diffraction grating is also of several types. The first typist transmission grating and the other is reflection grating.
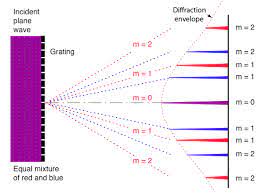
In the above picture, we can see the pattern due to diffraction grating. We can see that with the distance the height of the peak in the pattern decreases.
Different words related to grating
Transmission grating is well polished, thin, uniform, optically plane, and transparent glass plate which has equidistant Sharpe diamond points on it. When the ruling is made on a polished metal surface it is called a reflecting grating.
On the grating surface, the numbers of lines usually vary from 2500 to 8000 per centimeter. To achieve this number a very special ruler machine is used which is very costly. In laboratories like in school and college, a copy of grating is used which is made up of celluloid film by casting.
In the grating, the lines drawn using the ruler behaves like an opaque space with two transparent spaces on both sides.
Grating element or grating constant:- consider white of clear space a and the optic space be then the distance between the corresponding points is (a+b)= d. This d is called the grating element or grating constant.
This diffraction pattern using grating is also based on Huygen’s principle of superposition. The value of intensity in diffraction slit is I= (A2a2 ) sin2X /X2 (sin2NY/sin2Y). In this equation, sin2X /X2 and sin2NY/sin2Y control the intensity in the diffraction pattern. The value of the maxima in this diffraction patter increases with the value of the number of slits (N). The condition of principle maxima in this pattern is given by (a+b)sinθ = mλ.
Different phenomenon due to diffraction of light
There are many applications of diffraction which we come true in our daily life. These applications involve the colors of the rainbow, the color of the sky, and many more. Diffraction makes most of the beautiful phenomenon in nature.
Different colors of light
The white light is a combination of seven colors. We cannot see it because the seven colors merge because of their speed and wavelengths. Even the dispersion of light is the proper proof regarding this but diffraction also helps in it.

When dispersion takes place from a water droplet or a prism there is a bending of light. That bending of light is due to the diffraction of light. To know more about the colors of light click here.
Formation of Holograms
Ok, so this hologram word is quite amazing, right? Every time we hear this word it seems kind of fascinating. You are wondering how hologram and diffraction are connected, so let me tell you that hologram is an application of diffraction. Holograms are mainly steady photographs of light are we can say it is a 3D projection of a photograph. But you will say that how can we click a steady photo of an object because light travels very fast?

Yes, indeed we cannot click a steady photo of the object. This can be explained by the example that if you click a photo using your smartphone and if you are in motion then the photo will become a blur. This hologram is the result of a phenomenon caused due to refraction called standing waves. The standing wave at the result of collision or interface between two different patterns. because light travels faster so if we will use to distracting patterns from two different waves we can easily produce a steady picture. And this steady picture is known as a hologram.
Redness of the Sun

All of us enjoy the beautiful view of sunrise or sunset right? Have you ever wondered why the sun appears red at sunset and sunrise whereas at other times it is shiny yellow? So this is also a result of the diffraction of light which is coming from the Sun. During the time of dusk and dawn, the dust particles or tiny particles in the sky increases. This leads to the bending of the sun rays and hence producing the red color.
Shadows of objects
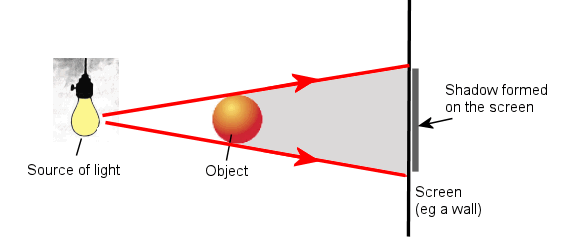
We can say that shadow of any object is also a result of the diffraction shadow of an object is formed because the light bends to the corner of the object and hence no light passes through that particular space which creates a shadow of it. This ultimately means that light cannot reach that place and hence create a black area which is known as the shadow.
Light comes in one room from another

I think you might have noticed when you switch on the light in one room, the light travels from that room to another. This is also the result of the diffraction of light. The light falls on the door of the room it bends and hence enters the other room. This happens because the light finds the door as an obstacle and bends itself.
Conclusion
Diffraction is a phenomenon that occurs every day in our lives. e notice different things which are the result of it. The major part of the properties which are processed by light. It results in some beautiful views of nature.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
In the visible spectrum of light, red is the most diffracted color among the all
Refraction is the change in the path of light when it travels from one medium to another. Whereas, Diffraction is bending of light when it encounters an object.
An Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi discovered diffraction during 1660.
White light is a mixture of several colors, hence it Is a polychromatic light.
Recent posts
- Protection from Coronavirus: Best Way to Secure Yourself (2020)
- Hydroelectricity: A massive source of electricity (2020)
- Lightsaber colors Mystery: Star wars Explained
- The Vibrant colors of light: True colors of light
- Virus: Definition, Structure, and Facts regarding virus
- The Big Bang Theory: Origin of the Universe


[…] Diffraction of Light: An Amazing phenomenon […]
[…] Diffraction of Light: An Amazing phenomenon […]